

Nitrogen (N):11%
P2O5:37%
pH:5.9
Density:1.421
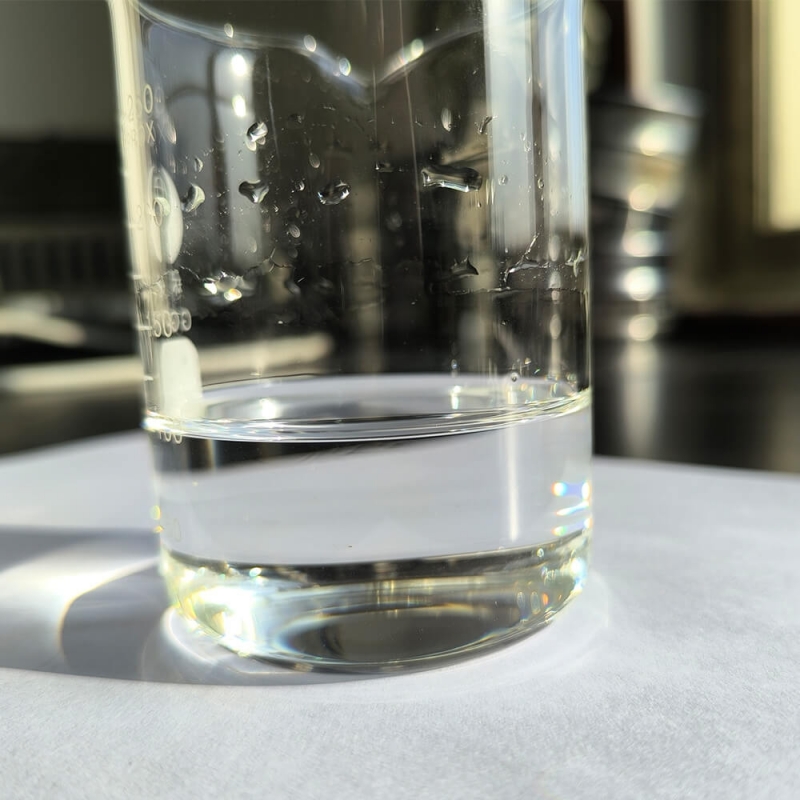
Color:Transparent Clear
Odor:no odor
Application method:Irrigation or Foliar Spraying
For Plants:All Plants and Crops
Absorbent:Instant absorbent
Package:1L, 200L, 1000L
Country of Origin:China
Ammnonia Polyphosphate Solution 11 – 37 – 0
(APS Nitrogen & Phosphorus Fertilizer )
Clear and transparent liquid solution, with no sediment.
Efficient and high-concentration nitrogen and phosphorus nutrients.
Nitrogen from ammonia sources; phosphates are slow-release to reduce leaching.
It can regulate the pH level by neutralizing and alleviating soil acidification.
Increase the stability of soil aggregates by interacting with minerals and organic matter in the soil.
Enhance the ability of plants to combat drought stress and biotic stress.
Promote photosynthesis efficiency and protein synthesis to achieve better growth.
What's Ammonia Polyphosphate Solution 11 37 0
Ammonium polyphosphate solution is a liquid containing ammonium polyphosphate (APP). Ammonium polyphosphate is an inorganic polymer containing
phosphorus and nitrogen in a chain-like structure, with the general molecular formula of (NH4)n +2PnO3n+1. In the solution state,
it usually appears as a colorless or light-yellow transparent liquid with a certain degree of viscosity. It is a highly efficient raw material for fertilizers,
rich in phosphorus and nitrogen elements, which enables it to have wide applications in both the agricultural and industrial fields.
Guaranteed Analysis
Nitrogen (N)--------------------11%
Phosphorus (P2O5)-------------37%
pH-------------------------------5.9
Density--------------------------1.421
Appearance: Clear and transparent liquid solution.
Directions For Use
There are multiple application methods for ammonium polyphosphate solution in agriculture:
Foliar spraying
Operation method: Dilute the ammonium polyphosphate solution with water at a certain dilution ratio, usually around 500 - 1000 times. For example, add 1 - 2 milliliters of
ammonium polyphosphate solution to each liter of water. Use spraying equipment, such as backpack sprayers or electric sprayers, to evenly spray the solution on both the front and back sides
of the plant leaves. Choose to spray in the early morning or late evening, and avoid operating when the sun is strong. Because intense sunlight may cause the solution to evaporate rapidly,
affecting the absorption effect and possibly burning the leaves at the same time.
Applicable scenarios and advantages: Foliar spraying enables plants to quickly absorb the phosphorus and nitrogen elements in the ammonium polyphosphate solution.
For some crops in the middle and late growth stages with weakened root absorption capacity, or when the soil environment is unfavorable for root nutrient absorption (such as overly dry or compacted soil),
foliar spraying is an excellent way to supplement nutrients. It can quickly correct the symptoms of nutrient deficiency in plants, such as yellowing leaves and slow growth,
and promote the photosynthesis of leaves, making the leaves greener and thicker.
Root irrigation
Operation method: It can be used through drip irrigation or flood irrigation. For drip irrigation, the ammonium polyphosphate solution needs to be mixed with irrigation water at an appropriate ratio.
Usually, add 0.5 - 1 kilogram of ammonium polyphosphate solution to each cubic meter of irrigation water. Through the drip irrigation system, slowly drip the mixed solution into the soil around the plant roots.
In the case of flood irrigation, after adding an appropriate amount of ammonium polyphosphate solution to the irrigation water, let the water flow naturally in the field so that the solution is
evenly distributed in the soil.
Applicable scenarios and advantages: Root irrigation is suitable for use at all stages of crop growth, especially in the early growth stage and the critical period of fertilizer demand.
This method allows the nutrients in the ammonium polyphosphate solution to penetrate into the soil around the plant roots along with the irrigation water and be directly absorbed by the roots.
Compared with other fertilization methods, it can deliver nutrients to the roots more accurately, reduce nutrient loss, and improve fertilizer utilization.
Moreover, ammonium polyphosphate can gradually hydrolyze in the soil, continuously providing phosphorus for plants to meet the long-term phosphorus requirements of crop growth.
© Copyright - 2021 | All Right Reserved. Designed By rutombio.com